This is the series of blog posts about the functional approach to cloud computations and big data using F# and MBrace framework.
Motivation
MBrace is fully open source framework written in F# and offers very clear and easy programming model. It aims to create all the necessary conditions to make distributed cloud scale computations and data as simple as possible. At the same time it is totally straightforward to setup MBrace clusters. In this series you will get the concept of "cloud monads" or cloud computation expressions, find out how to create a cluster and configure the environment, explore the features and opportunities we have with new F# functional cloud programming model and view the code of MBrace examples.
Background
Here, in the Part II of the series you will see the infrastructural options of creating the cluster for MBrace. If you want to know more about the concepts and the approach behind MBrace - it may be interesting to have a look at Part I.
What is MBrace
MBrace is a framework for big data and highly loaded computations. It is a programming model for scalable data scripting and data processing using F# and C#. It can be used on a public or private cloud. Azure cloud platform supports MBrace and it's absolutely easy to get Azure cluster for it using Brisk Engine. You can use your own data centers as well, so it is not limited to any cloud vendors.
Small note: Though MBrace is itself absolutely free, it implies and assumes using the underlying infrastructure and tools, which may require some costs. Sure, you can go with 100% free MBrace configuration using your own ecosystem, but it means you would have to perform all configurations and setup work fully by yourself. If you don't mind having some dirty work done for you by other clouds, like Azure with MBrace - you may want to pay for Azure cluster, which is now the most popular option for MBrace cluster. Anyway, all decisions are up to you and it's always the trade off between the comfort and cost.
How to start?
What do we need to start with MBrace?... Sure, you need a CLUSTER!
What options do you have? Actually, there is a big variety of options, it all depends on your goal and chioce.
- Custom cluster configuration
- MBrace on Windows Azure IaaS
- MBrace cluster using Brisk
Custom cluster configuration
If you decide to use custom machines, take into account that they should be visible on the same network. Each node should have:
- .NET Framework installed
- MBrace runtime installed
- Necessary firewall exceptions
- Ensuring
mbraced.exe.confighas correct settings. Example of this configuration file:
- MBrace windows service started and running
Azure IaaS cluster
Another option is to use Azure Infrastructure as a Service. If you have Azure subscription and account you may create a
Virtual Network following the instructions and then add the desired number of virtual machines there. After you have your cloud VMs created it is necessary to configure them as MBrace nodes with MBrace Runtime and correct settings in mbraced.exe.config file.
Both with Azure or custom cluster configuration there should be a client with MBrace runtime and F# - any F# supporting environment, e.g. F# Interactive, VS or any other - to initiate requests to the distributed system.
Brisk cluster for MBrace
There is another fancy one-click option - to use Brisk Engine. With Azure account you also can:
- Sign up on the Brisk website: https://www.briskengine.com/
- Click "Create new cluster" button and follow the instructions.
- Indicate the number of worker machines and other settings for the cluster.
There is also a wonderful tutorial how to use Brisk on Github.
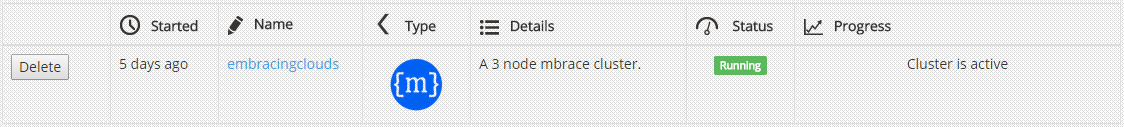
At this point the cluster is ready! Now it's time to set up a connection and prepare for boot.
Prepare to boot the cluster
If you are not using Brisk and use Azure IaaS or your specific machines, it is necessary to initialize the nodes. Here we have a list of nodes and connect to them using MBrace.Connect:
Here we specify either IP addresses or the nodes or the hostnames, with the ports, sure.
Another setting we'd like to indicate is the defaultStore, which our runtime will use. Currently, MBrace supports filesystem store...
... Azure store...
... and SQL Server store. So choose the suitable one. Now there is work in progress to add more store types available.
However, if you are using Brisk you can just go to Brisk administration page:
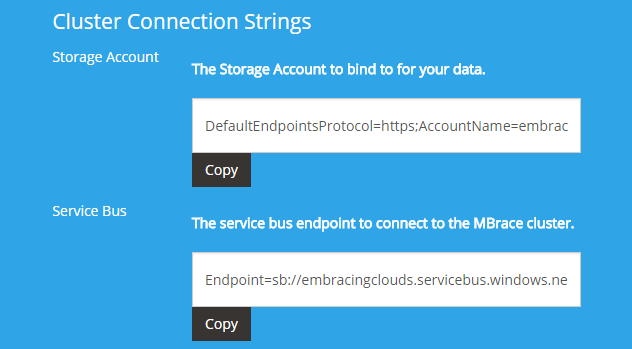
And indicate StorageConnectionString and ServiceBusConnectionString by copying those right from there:
Boot the runtime!
Now all the things are ready! The final step is to boot the runtime.
For custom cluster and Azure you can just use MBrace.Boot for the nodes, optionally specifying the store:
For Brisk you can use Runtime.GetHandle:
Congratulations!
We have everything ready to explore all the exciting features of MBrace. If you are curious - jump into the next part!